rfq-rag
A demo to share intuition for how RAG and LLM can be used to automate finance tasks that require written comprehension
Project maintained by parrisma Hosted on GitHub Pages — Theme by mattgraham
Automating Tedious Manual Finance Tasks with LLMs
Click here for Demo project repository & full code.
NOTES
- All data, names, and products in the demo are fictional and for illustration only.
- The financial products are partially defined, just enough to show differentiation.
Contents
- Overview
- Design & Approach
- Example LLM Prompt test it on your favourite WEB LLM
- Example Demo Run
- Deployment
- Demo Examples
- Concepts
Elusive Automation
It’s no news that the manual processing aspects of financial workflows are inefficient, error-prone, and costly. However, when written comprehension is required, automation often fails due to its rigidity and inability to adapt even to simple changes. So here, we show with a demo project (see below), how LLMs can be applied to address this long tail of manual processes that persists even after decades of automation.
Applied LLMs
LLMs bring automation potential but face key challenges:
- Missing Specifics: LLMs have vast general knowledge but lack real-time or company-specific knowledge essential for accurate financial task automation.
- Non-Determinism: LLM generative creativity can cause responses to vary, resulting in inconsistent automation inputs, the LLM model temperature paradox, see below.
- Explainability: Finance requires clear explanations for audits and compliance, which historical automation has not been able to supply, but at which LLMs excel.
The LLM Model Temperature Paradox
Imagine asking 100 journalists to summarize a breaking news story. You ask them to use their expertise but also provide consistent summaries. If they write too creatively, the summaries will vary wildly. If they think and write too rigidly, salient details may be missed.
This is akin to an LLM’s temperature setting: a high temperature setting promotes creativity but inconsistent results; a low temperature setting ensures consistency but reduces understanding and could miss key details. So, in any LLM automation, finding the right temperature setting is essential for reliable automation.
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
RAG enables LLMs to better understand written requests. It can incorporate proprietary and specialized knowledge into LLM Prompts, addresses explainability by detailing its reasoning and with the right model temperature, can produce deterministic results for automation.
Commodity Process
It’s now quick and cost-effective to build and deploy RAG solutions using readily available LLMs, private model hosting (even on PCs with GPUs!), and open-source or enterprise vector databases and other support tooling.
Intuition
Getting this intuition for RAG into the hands of those performing manual tasks it key, it allows their unique perspectives to shape its application, uncover opportunities, improve client services, and cut costs.
Conclusion
RAG has been around for a while but still has significant untapped applications in automating residual or enduring manual comprehension processes. We can tap this potential if we increase the intuition for the solution among those who are performing these manual tasks.
However, it’s not a free lunch:
- Much can be automated, but it does not 100% eliminate human oversight.
- Models and tooling are almost commodity, but specialists are required to use them.
- Compute costs could be a factor at scale, as running LLMs is very compute-intensive.
- Determinism is not guaranteed, so error detection must be designed in.
- Regulatory approval is an issue with customer-facing applications. (less so for internal ones)
- Models evolve quickly, so ongoing evaluation and selection are needed.
- Examples must be kept current as RAG is only as good as its augmentation data.
Demo: Parsing Requests for Quotes
As an example, consider automating the parsing of manual requests for quotes (RFQs) for structured products. We have created a demo that illustrates the approach’s potential.
The demo solution handles RFQs in English, French, and Spanish, including colloquial language, abbreviations, and typos, for two types of structured products, and delivers on:
- Specific Knowledge: Prompt augmented with related pre parsed RFQs.
- Determinism: Produces reliable JSON outputs for automation.
- Explainability: Clearly explains reasoning and assumptions.
We see RAG reliably processing complex language to automate a finance workflow.
Dive deeper into the project on our GitHub Pages to see how this is works!
Core Concepts
- Understanding
- LLMs grasp meaning, not just words, enabling interpretation of varied requests (e.g., “extract pricing terms”) across spoken languages, product types and colloquial variations.
- Augmentation
- LLMs use “meaning codes” (embeddings) to find semantically similar past examples in a database. These examples are added to prompts, improving accuracy with specific and validated knowledge.
- Explainability
- LLMs explain their reasoning and provide confidence scores, where low scores trigger human review, ensuring transparency and reliability.
Technology
- Ollama to run an host LLM’s.
- ChromaDB the vector database to support sematic augmentation.
- Langchain prompt building.
- Python as the glue language.
WorkFlow
The full workflow is shown below.
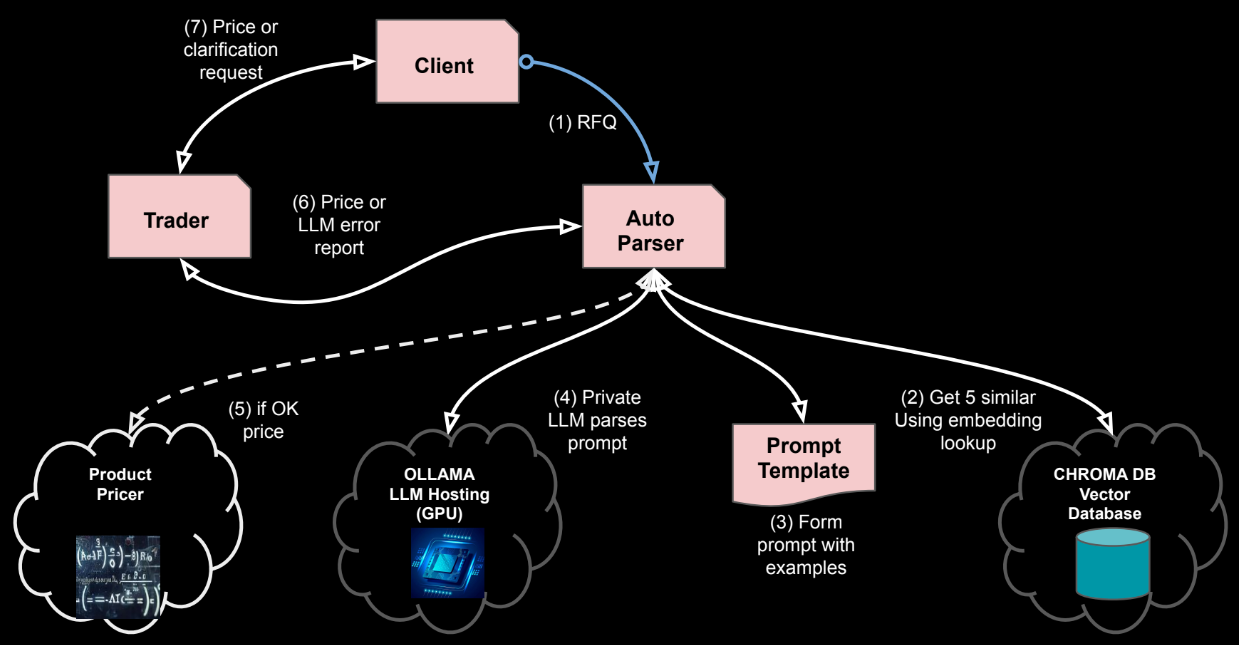
- RFQ From Client
- free text in any of three languages for two product types
- Get similar examples to client RFQ
- Use embeddings & vector DB to get semantically similar quotes
- Create the prompt with RFQ & examples
- Supply examples to prompt to give LLM specialist knowledge
- Ask LLM to extract parameters & explanation
- The explanation helps with the AI explainability problem if the result is questioned by client in the future
- If all OK price the product
- If extract is confident, we can auto price
- Pass price or error report to trader
- The price will be sent back, normally via person for sanity checks
- Trader can also look a clarification commentary from model
- Pass price or request for clarification with client